LAFCPUG: Glossary of Video Terms
From FAQwiki
Glossary of Video Terms: A-H
(Work in progress)
Please note : Many of the terms and definitions contained within this glossary are copyright Apple Computer Inc. and may not be reproduced without permission from Apple. Items listed in blue are LAFCPUG moderator contributed definitions.
Numerical
2:2:2:4 pull-down : An efficient but low-quality pull-down method, primarily useful for
previewing the output of real-time effects on an NTSC monitor. See also pull-down
insertion, pull-down pattern.
2:3:2:3 pull-down : The most commonly supported pull-down pattern for NTSC devices. This option is ideal for recording to an NTSC device such as standard definition television, an MPEG-2 encoding device, or a high-end finishing system. See also pull- down insertion, pull-down pattern.
2:3:3:2 pull-down : The pull-down pattern used by DV devices that support advanced pull-down. See also pull-down insertion, pull-down pattern.
24@25 pull-down : A pull-down pattern used in Final Cut Pro when 24 fps media is sent to a 25 fps video output. In this pattern, 12 progressive frames are displayed, followed by 13 re-interlaced frames.
24@25 repeat : A pull-down pattern used in Final Cut Pro when 24 fps media is sent to a 25 fps video output. In this pattern, 24 progressive frames are played and the 25th frame is the 24th frame repeated.
3:2 pull-down : See 2:3:2:3 pull-down.
4:3 : The aspect ratio for broadcast video. The ratio of the width to the height of the visible area of the video frame, also called the picture aspect ratio, is 4:3, or 1.33.
8-bit precision : For video, a bit depth at which color is sampled. 8-bit color is common with DV and other standard definition digital formats. Some high definition acquisition formats are also recorded with 8-bit precision.
10-bit resolution : For video, a bit depth at which color is sampled. Certain standard and high definition video capture interfaces are capable of uncompressed, 10-bit capture.
16-bit resolution : A standard bit depth for digital audio recording and playback.
16:9 : A widescreen aspect ratio for video. The ratio of the width to the height of the visible area of the video frame, also called the picture aspect ratio, is 16:9, or 1.78. The 16:9 aspect ratio is used for high definition video.
16 mm : A film format for film and television presentations, which has a 4:3 aspect ratio.
24-bit resolution : A bit depth used for high-quality audio playback. 32-bit floating point resolution : An extremely high resolution bit depth used for lossless computation of audio or video data.
35 mm : A standard motion picture film format. This may be cropped during projection to create widescreen aspect ratios such as 1.66 or 1.85, or filmed and projected anamorphically for an aspect ratio of 2.40.
65 mm : A film format for shooting widescreen presentations. This format is usually printed with a soundtrack onto 70 mm film.
70 mm : A film format for widescreen projections, which has a 2.2:1 aspect ratio.
180-degree rule : When a new camera angle is more than 180 degrees different from the previous camera angle, a shot with two people will appear to reverse positions onscreen. When editing a scene with two people talking, it’s important not to cut to a shot that crosses the 180-degree line that connects them.
A
action safe area: 90% of the image area. Most of the time, anything in your video
image that’s outside of this area won’t be displayed on a television screen, so any important
material needs to be framed within the action safe area. Compare with title safe area. See overscan.
Adjust Line Segment pointer : A cross-shaped pointer that appears in the Timeline and Viewer when you move the pointer over a line that can be adjusted, such as a line segment between keyframes. The pointer has small arrows pointing up and down, indicating the directions in which a line can be moved.
advanced pull-down : See 2:3:3:2 pull-down.
AIFF (Audio Interchange File Format) : A cross-platform file format supported by a large number of digital video and audio editing applications. You can reduce the file size of AIFF files with compressors, although this reduces the quality. AIFF audio can use a variety of bit depths, but the three most commonly used are 8-,16-, and 24-bit.
alpha channel : An image channel in addition to the R, G, and B color channels that is used to store transparency information for compositing. Alpha channels are often 8-bit, but some applications support 16-bit alpha channels. In Final Cut Pro, black represents 100 percent transparency, and white represents 100 percent opacity. Only certain formats, such as Targa, TIFF, PICT, and the QuickTime Animation codec, support alpha channels.
alignment : When working with transitions, refers to whether the transition starts before the edit point, is centered at the edit point, or ends after the edit point.
ambience : A type of sound. Ambient audio includes background room noise, traffic noise, and atmospheric sound effects.
analog or analogue : A signal that consists of a constantly varying voltage level, called a waveform, that represents video and audio information. Analog signals must be digitized, or captured, for use by Final Cut Pro. VHS and Betacam SP are both analog tape formats. Compare with digital.
anamorphic : Visuals that are shot in a widescreen format and then squeezed into a 4:3 frame size. This can be done by using a video camera’s electronics or, optically, by using an anamorphic lens.
anchor item : When you first link multiple audio clip items to a video item in the Timeline, that video item is considered the “anchor” item to which the sync of all other linked audio items is compared. If you’re linking a group of audio items without a video item, the topmost audio item that appears in the Timeline acts as the anchor item.
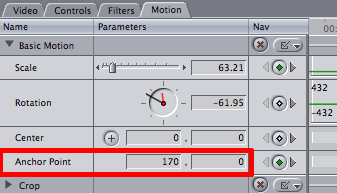
anchor point : In the Motion tab, the point that is used to center changes to a clip’s geometry when using motion effects. Any changes to the size, position, and rotation of a clip happen relative to this anchor point. A clip’s anchor point does not have to be at its center.
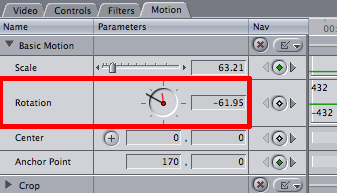
Angle control : A control used to rotate a clip around its center axis without changing its shape. Located in the Motion tab of the Viewer. In the Angle control, the black hand indicates the current angle of the clip, and the small red hand indicates how many total rotations forward or backward have been specified.
A-only edit : An edit of the audio files or video files of the base track only.
A-roll edit : An edit of clips that contain audio data from the base track or a narration.
aspect ratio : A film or video frame’s width-to-height ratio on any viewing screen. The most common aspect ratio is 4:3, used for regular television screens. An aspect ratio of 16:9 is increasingly used for high definition video.
assemble edit mode : In linear systems, assemble edit mode lays down new video, audio, and control tracks all at once. It usually requires anywhere from 3 to 5 seconds of pre-roll before you edit to tape. In Final Cut Pro, assemble edit mode is a function that writes the sequence or clip to tape at the designated In point, or at the current point. Assemble edit mode usually breaks the timecode and control track at the end of the edit.
attenuate : To lower an audio signal’s level.
audio channel indicator : An icon in the Edit to Tape window that indicates which audio tracks are being output.
audio clip : A media clip containing audio tracks.
audio meter : A meter that lets you monitor audio output levels from your computer. You use the audio meters in Final Cut Pro when you capture, mix, and outputting your program.
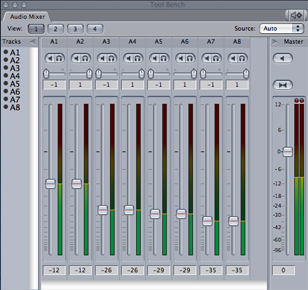
Audio Mixer : A tab in the Tool Bench window. The Audio Mixer is the primary tool in Final Cut Pro for mixing multiple channels of a program’s audio in real time.
audio track : A track in the Timeline into which you can edit audio clip items.

Audio Units : The standard real-time audio filter format for audio applications running on Mac OS X.
Auto Render : A feature that allows Final Cut Pro to render open sequences whenever a specified number of idle minutes have passed.
Auto Select control : Enabling the Auto Select controls of specific tracks in the Timeline limits which tracks are affected by various functions such as copying, pasting, deleting, the Match Frame command and so on.
Note: You can think of In and Out points as limiting your edits in the horizontal (time) dimension and Auto Select as limiting your edits in the vertical dimension.
average loudness : The average audio level in decibels. Determines the apparent volume of an audio signal to a listener.
averaging meter : A meter that displays the average audio level. Unlike peak meters, which always show the exact level of an audio signal including every peak, averaging meters have weighted ballistics so that they give a more readily apparent representation of the average loudness of an audio signal.
AVI (Audio-Video Interleaved) : Microsoft’s older standard format for digital video. It is a filetype "wrapper" and like Quicktime .mov, .avi can contain a variety of CODECs such as DV, DiVX, Indeo® Video...
axis : The pitch, roll, and yaw of a camera shot determines its axis. In an edited sequence, the axis can be used to determine visual continuity from shot to shot.
B
back light : A light source that comes from behind and above the subject. It outlines
the subject and differentiates it from the background. Also called a rim light.
batch capture : A process in which previously logged clips’ media is captured from a VTR or camcorder to your hard disk. The timecode in each clip is used to automatically cue source tapes, using remote device control, to the location of each clip.
batch compression : A process in which multiple clips or sequences are automatically compressed to new media files, without manually overseeing each one.
batch list : A tab-delimited text file that contains information about offline clips that you want to capture and use in your project. Batch lists can be exported from or imported into your Final Cut Pro project file. After you import a batch capture list into Final Cut Pro, your project contains a series of offline clips, one for each entry in the batch capture list. You then need to recapture or reconnect the clips to their media.
batch recapture : A process in which you recapture, at a higher resolution, the parts of logged clips that you actually use in your sequences. Helps to conserve disk space.
Betacam SP : A high-end, standard definition component analog video format.
Supports four tracks of analog audio. Note that Sp Beta boxes and tapes are grey.

Betacam SX : A standard definition, 8-bit digital videotape recorder format with 10:1 video compression using MPEG-2 compression, and 4:2:2 color sampling. Supports four tracks of audio with 16-bit, 48 kHz audio sampling. Note that SX Beta boxes and tapes are yellow.

Bezier curve : In its simplest form, a line defined by two end points and two associated control points, or “handles”. Pulling the control points adjust the line into a curve. Named after Pierre Bezier, who discovered the mathematical formula for these curves. In Final Cut Pro, Bezier curves are used to adjust keyframed effects and to create curves in motion paths.
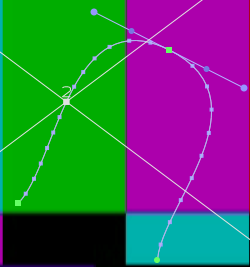
Bezier handles : Controls that let you modify the curve of a line segment between a handle and the next point on either side of it. The farther a handle is dragged from its vertex point, the more it bends or curves the line segment. Used for smoothing keyframes.
bin : A container (or folder) inside of the Browser that can contain clips, sequences, transitions, effects, and generators. You use bins to organize these elements, sort them, add comments, rename items, and so on.
black level : An analog video signal’s voltage level for the color black, represented by IRE units. Absolute black, or setup, is represented by 7.5 IRE for NTSC in the United States and 0 IRE for NTSC in Japan and for PAL.
blue or green screening : A special effects technique that allows you to derive an alpha channel or matte from the blue or green background of a video clip in order to make it transparent for purposes of compositing against other clips. Blue-screen technology is what makes weather forecasters appear to be standing against an animated map, when in reality they’re standing in front of a blue wall. Also known as chroma keying. See also keying.
boosting : The act of raising an audio level.
boundary : Refers to either the In or Out point of a clip in the Timeline.
bounding box : An 'invisible' box that surrounds an image or group of images and defines their edges. Useful for moving or distorting items in the canvas.
broadcast : Refers to signals intended for delivery on television, as well as network delivery to a wide audience. Broadcasters may have strict guidelines for the signal quality of programs for air. Broadcast quality is a phrase often used when referring to these guidelines.
broadcast legal : Broadcast facilities have limits on the maximum values of luma and chroma that are allowable for broadcast. If a video exceeds these limits, distortion can appear, resulting in unacceptable transmission quality. You can use the Final Cut Pro video scopes and range-checking options to make sure that the luma and chroma levels you set stay legal.
B-roll : A term used to describe alternate footage shot to intercut with the primary shots used in a program. B-roll is frequently used for cutaway shots.
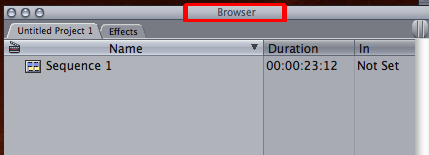
Browser : The central storage area in Final Cut Pro, where you organize all of the source material used in your project. The Browser lists all elements—video and audio clips, graphics clips, and sequences—in a project. Each project is represented by a tab that contains that project’s file. You can further organize your media clips within a project using bins, which are similar to folders.
C
calibrate : To adjust a feature for accuracy.
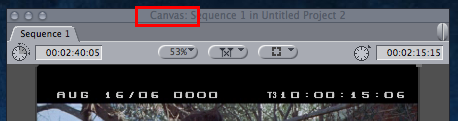
Canvas : In Final Cut Pro, the Canvas is the equivalent of a record monitor in a tape-to-tape editing system. It works with the Timeline, displaying the frame at the position of the playhead in the Timeline and showing what your edited sequence looks like when it is played. Changes you make to a sequence in the Timeline are seen when you play back that sequence in the Canvas. If you modify clips in the Canvas, the changes are stored with the clips in the Timeline. You can also use the Canvas to perform edits.
capture : To move NTSC or PAL video or audio from tape to a digital format for use by Final Cut Pro. An older term for capturing is digitizing. Captured video clips appear on the specified scratch disk as a series of QuickTime movie files. See also digitize.
center point : Defines a clip’s location in the X/Y coordinate space in the Motion tab of the Canvas.
CG : Abbreviation for Character Generator. A specialized hardware device used for creating titles.
CGI : Abbreviation for Computer-generated imagery.
channel 1 : Typically the left audio channel in a stereo recording.
channel 2 : Typically the right audio channel in a stereo recording.
channels : When used to describe video, can refer to color channels or alpha channels. Color and transparency information for video and graphics clips is divided into individual channels. Each individual color channel represents one of the three individual primary colors that mix together to represent the final image. Each channel has a bit depth; most graphics and video files are 8 bits per channel, meaning that there are 256 levels of color or transparency for each channel.
chip chart : A grayscale chart that is placed next to the slate at the beginning of every shot. During postproduction, the color chart can be used to correct each shot so that the whites, blacks, and colors can be perfectly reproduced during editing.

chroma : The color information contained in a video signal, consisting of hue (phase angle), which represents the color itself, and saturation (amplitude of the color subcarrier), which represents the intensity of the color.
chroma keying : See blue or green screening.
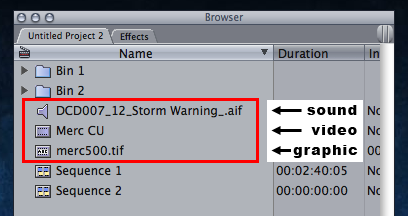
clip : An item in a Final Cut Pro project representing video, audio, or graphics media files on disk.
clipping : Distortion occurring during the playback or recording of digital audio because of a signal that exceeds the maximum sample value of 0 dBFS.
CMYK : Abbreviation for Cyan Magenta Yellow Black. The color space commonly used for images that are printed with four-color ink on offset presses.
CODEC or codec : Short for compressor/decompressor, or encode/decode. A software component used to translate video or audio from its analog uncompressed form to the digital compressed form in which it is stored on a computer’s hard disk. DV, Photo, JPEG, and Sorenson Video are common QuickTime video codecs. Also referred to as a compressor.
color balance : Refers to the mixes of red, green, and blue in a clip. In Final Cut Pro, you can adjust the color balance of the highlights (bright areas), midtones, or shadows (dark areas) of your clip using the Color Corrector 3-way filter.
color bars : A standard color test signal displayed as columns, often accompanied by a reference audio tone. Color bars are used to adjust the video signal of the incoming source tape to maintain proper color from tape to computer and through to output. Color bars are also output to a master tape so that accurate duplicates (dubs) of the tape can be made.

color correction : A process in which the color of clips used in an edited program is evened out so that all shots in a given scene match. Color correction is generally one of the last steps in finishing an edited program. The color correction tools in Final Cut Pro give you precise control over the look of every clip in your project by adjusting the color balance, black levels, mids, and white levels of individual clips.
color depth : The possible range of colors that can be used in a movie or image. There are generally four choices with computer graphics— 8-bit (grayscale), 16-bit, and 24-bit (millions of colors). Higher color depths provide a wider range of colors but require more space for a given image size. Broadcast video is generally 24-bit, with 8 bits of color information per channel. See also channels.
colorist : A professional who performs color correction. The colorist, in consultation with the cinematographer, director, or producer, works shot by shot to determine the look of each clip according to the needs of the project.
component video : A type of analog video signal in which the luma and chroma signals are recorded separately for better video quality. Professional video equipment, such as a Betacam SP deck, uses component Y?CRCB (also called component YUV) video inputs and outputs. Another form of component video, component RGB, is not as widespread on video gear as component Y?CBCR.
composite video : An analog video signal that combines all chroma and luma information into a single waveform running through a single cable. This can result in analog “artifacts,” affecting the quality of the video signal. Nearly all video equipment has composite inputs and outputs.
compositing : A process in which two or more images are combined into a single frame. This term can also describe the process of creating various video effects.
compression : The process by which video, graphics, and audio files are reduced in size. “Lossy” compression refers to a process of reducing video file sizes through the removal of redundant or less noticeable image data. Lossless compression reduces file sizes by mathematically consolidating redundant image data without discarding it. See also codec.
contrast : The difference between the lightest and darkest values in an image. High-contrast images have a large range of values from the darkest shadow to the lightest highlight. Low-contrast images have a more narrow range of values, resulting in a “flatter” look.
coverage : A series of medium shots and close-ups, taken after the master shot, all of which cover the same material in the script. Used when shooting a scene with continuity. These shots are called coverage because they’re often used to cover different edits made in the scene.
crop : To mask a specified amount from the total frame size of an image. You can crop the top, left, right, and bottom of an image independently.
cut : An edit in which one clip immediately follows another, with no transition effect. This is the simplest type of edit.
cutaway shot : A shot that is related to the current subject and occurs in the same time frame. For example, an interviewer’s reaction to what is being said in an interview is a cutaway shot. Often, a cutaway shot is used to eliminate an unwanted visual section of another shot. The audio usually remains continuous, helping to make the cutaway less noticeable.
D
D1 : Has 2 definitions, see below.
1. A standard definition digital videotape recorder format that records an 8-bit uncompressed component video signal with 4:2:2 color sampling. Conforms to the ITU-R BT 601 4:2:2 format (formerly CCIR-601). Recorded using 19 mm tape. Supports four tracks of audio.
2. D1 is often used to describe the standard pixel dimension and display ratio used in PAL & NTSC Standard Definition digital video. D1 NTSC is 720x486 pixels (40:27) and displayed 4:3 D1 NTSC widescreen is also 720x486 pixels (40:27) but displayed as 16:9 anamorphic D1 PAL is 720x576 pixels (5:4) and displayed 4:3 D1 PAL widescreen is also 720x576 pixels (5:4) but displayed as 16:9 anamorphic.
D2 : A standard definition digital videotape recorder format that records an 8-bit uncompressed composite video signal with 4Fsc color sampling. Recorded using 19 mm tape. Supports four tracks of audio.
D3 : A standard definition digital videotape recorder format that records an 8-bit uncompressed composite video signal with 4Fsc color sampling. Recorded using 1/2 inch tape. Supports four tracks of audio.
D5 : A standard definition digital videotape recorder format that records a 10-bit uncompressed component video signal with 4:2:2 color sampling. Recorded using 1/2 inch tape. Supports four tracks of audio.
D9 : Also known as Digital-S. A standard definition digital videotape recorder format that records an 8-bit, 2:1 DCT compressed component video signal with 4:2:2 color sampling. Recorded using 1/2 inch tape. Supports four tracks of audio.
data rate : The speed at which data can be transferred, often described in megabytes per second (MB/sec.) or megabits per second (Mbps). The higher a video file’s data rate, the higher quality it will be, but the more system resources (processor speed, hard disk space, and performance) it will require. Some codecs allow you to specify a maximum data rate for a movie during capture.
DAW (Digital Audio Workstation) : A digital editing and recording device or software application used for editing multitrack audio for music or audio postproduction.
decibel (dB) : Unit of measurement for sound levels; a logarithmic scale used to describe the loudness of sound as perceived by the human ear. (1 dB corresponds to approximately the smallest volume change that the average human ear can perceive.) For digital audio, dBFS is the standard decibel unit of sound level measurement. See also digital full scale.
decompression : The process of creating a viewable image for playback from a compressed video, graphics, or audio file. Compare with compression.
desaturate : To remove color from an image. 100 percent desaturation results in a grayscale image.
destination track : The track a particular source item is edited into in the Timeline, as defined by the Source and Destination controls in the Timeline patch panel.
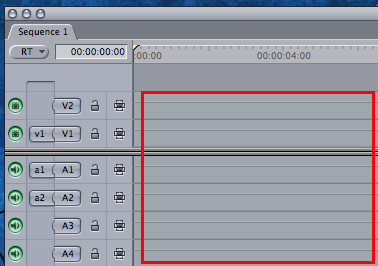
destination track controls : Source and Destination controls in Timeline tracks that allow you to specify which tracks source clip items are edited into in the Timeline.
device control : Technology that allows Final Cut Pro to control an external hardware device, such as a video deck or camera. Three protocols are used most frequently to control video devices: serial device control via the RS-422 and RS-232 protocols, and FireWire for DV camcorders and decks.
dialogue : The recorded audio of one or more people speaking in a video clip. The designated dialogue track in an editing project is likely to include most of the location audio that was captured along with the video.
digital : A description of data that is stored or transmitted as a sequence of 1s and 0s. Most commonly, refers to binary data represented using electronic or electromagnetic signals. QuickTime movie files are digital. Compare with analog.
Digital-8 : A standard definition consumer digital video format that records a DV video signal onto Hi-8-style tapes.

Digital Betacam : A standard definition 10-bit digital videotape recorder format with 2:1 video data compression and 4:2:2 color sampling. Supports four tracks of audio with 20-bit, 48 kHz audio sampling. Note that (Sony) Digibeta boxes are blue, and the tapes are grey and black.

digital full scale : The full audio signal range that can be recorded digitally without distortion.
Digital-S : See D9.
digital video : Video that can be captured, manipulated, and stored using a digital format, such as QuickTime. A digital video camcorder, for example, is a video camera that records images digitally on a medium such as tape. Because the signal is digital, it can be easily transferred to your computer.
digitize : To convert an analog video signal into a digital video format. A method of capturing video. See also capture.
disabled track : A track that has had its Track visibility control disabled. Disabled tracks will not output to tape or be rendered into a QuickTime file for output.
disclosure triangle : A small triangle you click to show or hide details in the interface.
distort : To change the shape of a clip by moving a corner point independently of the other corner points. Also, to squeeze a clip horizontally or vertically to change the ratio of its width to its height (the aspect ratio).
downmixing : Also referred to as mixing down, the process used to combine multiple audio channels to a single stereo (or dual mono) pair.
DPI : Dots Per Inch Is the measure of how many individual printed dots per inch of paper are printed out. It is also the number of pixels scanned per inch of source material. It has no bearing in video except where you print out or scan in.
Please read the FAQ on DPI
drop frame timecode : NTSC timecode that skips ahead in time by two frame numbers each minute, except every tenth minute, so that the timecode agrees with the actual elapsed clock time. (Timecode numbers are skipped, but actual video frames are not skipped.) This skipping corrects for NTSC’s actual frame rate of 29.97 fps. It corrects for an inaccuracy of 3 seconds and 18 frames per hour in comparison to actual elapsed time when non-drop frame timecode is used. To avoid confusion, dropframe timecode should be avoided in film-based productions. Compare with non-drop frame timecode.
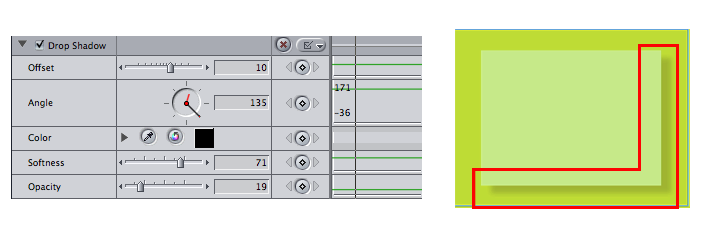
drop shadow : An effect that creates an artificial shadow behind an image. Typically used with graphics and text.
dual system recording : A recording process in which video is captured on one recording device and audio is recorded on another. Dual system audio must be synchronized onto the source videotapes prior to capture, or synced up in Final Cut Pro.
duplicate frames indicator : Colored bar that appears at the bottom of a clip’s video item in the Timeline, indicating that frames are duplicated elsewhere in the sequence. Useful for editing film where duplicate frames can cause complications during the final negative cut.
duration : The length of time between a clip’s In and Out points.
DV : Digital Video. A standard definition digital videotape recorder format that records an 8-bit, 5:1 compressed component video signal with 4:1:1 color sampling (PAL uses 4:2:0). Recorded using 1/4 inch tape. Supports two tracks of audio with 16-bit, 48 kHz audio sampling, or four tracks of audio with 12-bit, 32 kHz audio sampling.

DVCAM : A standard definition digital videotape recorder format that records an 8-bit, 5:1 compressed component video signal with 4:1:1 color sampling (PAL uses 4:2:0). Recorded using 1/4 inch tape. Supports two tracks of audio with 16-bit, 48 kHz audio sampling, or four tracks of audio with 12-bit, 32 kHz audio sampling.

DVCPRO : A standard definition digital videotape recorder format that records an 8-bit, 5:1 compressed component video signal using 4:1:1 color sampling (PAL uses 4:2:0). Recorded using 1/4 inch tape. Supports two tracks of audio with 16-bit, 48 kHz audio sampling. Note that DVCPro tapes also come with red, blue and grey tops. These are indications of the tape size, not the format, and can all be used for DVCPro, DVCPro 50 and DVCPro HD.

DVCPRO 50 : A standard definition digital videotape recorder format that records an 8-bit, 3.3:1 compressed component video signal with 4:2:2 color sampling. Recorded using 1/4 inch tape. Supports four tracks of audio with 16-bit, 48 kHz audio sampling.
DVCPRO HD : A high definition video format that records an 8-bit compressed component video signal with 4:2:2 color sampling. Both 720p and 1080i are supported. Includes up to eight tracks of audio with 16-bit, 48 kHz audio sampling. Recorded using 1/4 inch tape. The total data rate is 100 Mbps.
DVD : Digital Versatile Disc. A disc that is the size of a CD, but that uses higher density storage methods to significantly increase its capacity. Although usually used for video distribution, DVD-ROM discs can also be used to store computer data.
dynamic range : The difference, in decibels, between the loudest and softest parts of a recording.
E
EDL (Edit Decision List) : A text file that uses the source timecode of clips to sequentially list all of the edits that make up a sequence. EDLs are used to move a project from one editing application to another, or to coordinate the assembly of a program in a tape-based online editing facility.
editing : The process of combining and arranging audio, video, effects, transitions, and
graphics in a sequence to produce a program.
edit point : (1) Defines what part of a clip you want to use in an edited sequence. Edit points include In points, which specify the beginning of a section of a clip or sequence, and Out points, which specify the end of a section of a clip or sequence. (2) The point in the Timeline in an edited sequence where the Out point of one clip meets the In point of the next clip. This edit point can be selected for various operations.
Edit to Tape : In Final Cut Pro, the Edit to Tape command lets you perform frame- accurate insert and assemble edits to tape.
effects : A general term used to describe all of the Final Cut Pro capabilities that go
beyond cuts-only editing. See filters, generators, and transitions.
exposure : The amount of light in video or film images. Exposure affects the overall brightness of the image as well as its perceived contrast.
extend edit : An edit in which the edit point is moved to the position of the playhead in the Timeline. It allows you to move an edit point between two clips quickly. An extend edit overwrites any clips that come between the selected edit point and the playhead. It does not affect the overall duration of a sequence.
eyeline match : During the intercutting of shots, refers to cutting from a clip of a person looking at something to a clip containing the object that is being looked at.
F
faders : In the Audio Mixer, vertical sliders used to adjust the audio levels of clips at the position of the playhead. Using the fader, you can adjust the audio level of a clip on a smooth logarithmic scale ranging from +12 dB to –Inf dB (otherwise known as silence.)
favorite : A customized effect that is used frequently. You can create favorites from most
of the effects in Final Cut Pro.
field : Half of an interlaced video frame consisting of the odd or the even scan lines. Alternating video fields are drawn every 1/60th of a second in NTSC video to create the perceived 30 fps video. There are two fields for every frame, an upper field and a lower field.
filters : Effects you can apply to video or audio clip items. Filters affect the visual or aural quality of the clip to which they’re applied. For example, a video filter might change the colors of your image, while an audio filter might add some reverberance, making actors sound as if they’re in a huge space. In addition to using the filters that come with Final Cut Pro, you can use third-party filters.
finishing : The process of reassembling the clips used in the final edit of a program at
their highest quality. Finishing may involve recapturing offline resolution clips at full
resolution, rerendering effects, then outputting the final program to tape. Finishing
may also involve extra steps that were not taken in the offline edit, such as color
correction.
finishing on tape : The process of using the EDL from an offline edit to reassemble a sequence from the original source tapes in an online tape-to-tape editing suite.
FireWire : The trademarked Apple name for the IEEE 1394 standard. A fast and versatile interface used to connect DV camcorders to computers. FireWire is well suited to applications that move large amounts of data, and can also be used to connect hard disks, scanners, and other kinds of computer peripherals.

fit to fill edit : An edit in which a clip’s speed is adjusted to fit a specified duration in a sequence.
flesh tone : A special marker in the Final Cut Pro Vectorscope that indicates an area of appropriate range for all shades of skin color. When calibrating a tape’s color in preparation for capture or when using one of the color corrector tapes, the flesh tone marker can be used as a guide for adjusting the hue in order to make sure the skin tones look correct.
frame : A single still image. Film and video are made up of a series of these images.
While a film frame is a single photographic image, an interlaced video frame contains
two fields.
frame blending : A process of visually averaging frames together over time to create smoother motion. This is often useful when playing back clips in slow motion, to smooth otherwise jerky motion.
frequency : The number of times a sound or signal vibrates each second, measured in cycles per second, or hertz (Hz). Audio recordings are made up of a vast collection of waveforms, using many different frequencies of sound. Each frequency in a recording is associated with an audio pitch. For example, the note generated by each key of a piano is at a specific frequency.
G
gain : The amount an audio or video signal is boosted. In video, this increases the white level; in audio, this increases the volume.
gamma : A curve that describes how the middle tones of an image appear. Gamma is a nonlinear function often confused with “brightness” or “contrast.” Changing the value of the gamma affects middle tones while leaving the whites and blacks of the image unaltered. Gamma adjustment is often used to compensate for differences between Macintosh and Windows video graphics cards and displays.
ganged : The behavior of the playheads in the Viewer and Canvas when they’re locked together, so that they move as one.
gaps : Locations in a sequence where there is no media on any track. When output to video, gaps in an edited sequence appear as black sections.

gear down : To slow down a mouse operation and make it more precise by holding down the Command key while dragging an item or control. This can be helpful when dragging clips if, for example, the Timeline is zoomed out so that clips look small. It’s also useful to gear down if you want to make very small changes to an edit point, a keyframe parameter, or a volume level.
generators : Clips that are synthesized by Final Cut Pro. Generators can be used as different kinds of backgrounds, titles, and elements for visual design.
H
handles : Extra footage beyond a clip’s In and Out points. Handles are useful if you want to add a few more frames to account for dissolves or additional trimming.
HDCAM : A high definition digital videotape recorder format that records an 8-bit, 7.1:1 DCT compressed component video signal with 3:1:1 color sampling. Recorded using 1/2 inch tape. Supports four tracks of audio.

HDV : An MPEG-2–based high definition video format that records on a DV cassette
tape. HDV supports both 720p and 1080i, and uses interframe (or long-GOP MPEG-2)
compression. Depending on the format, HDV has a data rate of 19 Mbps or 25 Mbps.

Note : HDV can also be recorded on standard DV tape.
head clip : The clip that begins a sequence.
headroom : 1. The available range in decibels (dB) that falls in between the reference level
that is used to denote the average loudness of a mix and 0 dBFS. If you mix your
project with the reference level set to –12 dBFS, you have 12 dB of headroom available
before the signal is clipped. If the audio in a sequence has a wide dynamic range, you
set the reference level low enough to create enough headroom so that no part of the
signal goes above 0 dBFS.
2. The amount of space between the top of a subject's head and the top of the frame when shooting.
Hi-8 : An analog videotape format. Introduced as a higher quality version of 8 mm.

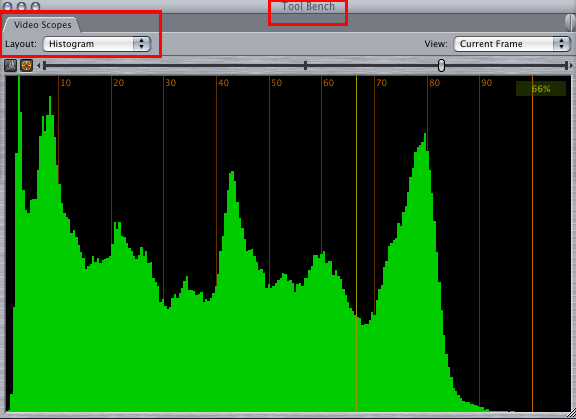
Histogram : A video scope in Final Cut Pro that displays the relative strength of all luma values in a video frame, from black to super-white. It is useful for comparing two clips in order to match their brightness values more closely.
hue : An attribute of color perception, also known as color phase. Red, blue, yellow, and green are all different hues.
==Glossary of Video Terms: I-P==