LAFCPUG: HD Formats FAQs
From FAQwiki
(→How do I work with P2 media?) |
(→What files are required when working with P2?) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 199: | Line 199: | ||
Here's a great simple video tutorial about P2 import by '''Shane Ross''' : [http://library.creativecow.net/articles/ross_shane/p2_workflow/video-tutorial.php Importing P2 into FCP]<br> | Here's a great simple video tutorial about P2 import by '''Shane Ross''' : [http://library.creativecow.net/articles/ross_shane/p2_workflow/video-tutorial.php Importing P2 into FCP]<br> | ||
| + | |||
Updated for FCP6: | Updated for FCP6: | ||
| - | [http://library.creativecow.net/articles/ross_shane/p2fcp6/video-tutorial.php Importing P2 into FCP6] by '''Shane Ross''' | + | *[http://library.creativecow.net/articles/ross_shane/p2fcp6/video-tutorial.php Importing P2 into FCP6] by '''Shane Ross''' |
| + | |||
| + | |||
Also: | Also: | ||
*[http://edu.moviola.com/mounting_p2_cards Problems Mounting P2 Volumes] by '''Andrew Balis''' | *[http://edu.moviola.com/mounting_p2_cards Problems Mounting P2 Volumes] by '''Andrew Balis''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Also: | Also: | ||
| Line 215: | Line 220: | ||
*[http://panasonic.sixbullets.net/ A quick and dirty download guide to Panasonic P2 drivers, firmware, utilities, and more] | *[http://panasonic.sixbullets.net/ A quick and dirty download guide to Panasonic P2 drivers, firmware, utilities, and more] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
From '''Strypes''' | From '''Strypes''' | ||
| Line 221: | Line 228: | ||
How to work with P2 in FCP: | How to work with P2 in FCP: | ||
| - | [ftp://ftp.panasonic.com/pub/Panasonic/Drivers/PBTS/papers/Apple_Final_Cut_Pro2008.pdf Using P2 HD with Final Cut] | + | *[ftp://ftp.panasonic.com/pub/Panasonic/Drivers/PBTS/papers/Apple_Final_Cut_Pro2008.pdf Using P2 HD with Final Cut] |
| Line 312: | Line 319: | ||
Read this article by Rick Young: | Read this article by Rick Young: | ||
| - | *[http://www.kenstone.net/fcp_homepage/ex1_sd_output_young.html Outputting Standard Definition in FCP from the Sony XDCam EX1] | + | *[http://www.kenstone.net/fcp_homepage/ex1_sd_output_young.html Outputting Standard Definition in FCP from the Sony XDCam EX1]<br> |
| + | |||
| + | and this by Matt Jeppsen<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[http://provideocoalition.com/index.php/freshdv/story/xdcam_ex1_hands_on_final_cut_pro_workflow/ XDCAM EX1 Hands-On - Final Cut Pro Workflow] | ||
| Line 320: | Line 331: | ||
[http://www.lafcpug.org/ Back to lafcpug.org] | [http://www.lafcpug.org/ Back to lafcpug.org] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==What files are required to work with P2?== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''From Strypes''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Final Cut Pro's Log and Transfer requires the entire directory to be present to work properly with P2 media, including the LASTCLIP.TXT file. By default, the "PROXY" and "VOICE" folders are empty. The "AUDIO" folder contains the audio recorded in the camera, the "VIDEO" folder contains the video clips, the "ICON" folder contains thumbnails, and the "CLIP" folder contains XML files with the required metadata to sync up the video and audio files. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here is a breakdown of the directory structure: | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''<Card Name>''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | LASTCLIP.TXT | ||
| + | <CONTENTS> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <AUDIO> | ||
| + | <CLIP> | ||
| + | <ICON> | ||
| + | <PROXY> | ||
| + | <VIDEO> | ||
| + | <VOICE> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.lafcpug.org/faqwiki/index.php?title=LAFCPUG:_HD_Formats_FAQs Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents]<br> | ||
| + | [http://www.lafcpug.org/faqwiki/index.php/Main_Page Back to Index of FAQs]<br> | ||
| + | [http://www.lafcpug.org/ Back to lafcpug.org] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Latest revision as of 17:17, 18 January 2009
Can't capture HDV Video.
From Jude Cotter
If you're trying to capture HDV footage into FCP and all you get is a black screen, check if your deck or camera is set to 'i-Link Conversion'. This setting causes the deck or camera to down-convert HDV to DV automatically. If this is not what you want, turn it off. Also, make sure that your project is set up to capture HDV, not DV.
More detail from Christina A
With the Canon XH A1 you CANNOT change the settings that you need to change if the camera has the FireWire cable plugged into it.
- 1. You first need to disconnect the FireWire cable, then put your camera on VCR/Playback mode.
- 2. Click on the menu button and go to SIGNAL SETUP. (Since you do not have the FireWire cable plugged in, you can NOW change two important settings needed to import HD footage).
- 3. Under SIGNAL SETUP, scroll down to PLAYBACK STD. Click on that and make sure the HDV is set. NOT the AUTO, it most likely will not import under AUTO. Once the HDV is set, you're half-way there.
- 4. Next go back to SIGNAL SETUP and scroll down to HD DOWN-CONV and click on this. Make sure it is OFF. Once you set this, you're done.
- 5. Go back to SIGNAL SETUP and check this settings to make sure they read:
- PLAYBACK STD HDV
- HD DOWN-CONV OFF
- 6. You can now plug in your FireWire cable and you will see after a few seconds that these settings turn "gray" and you cannot change them.
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
Understanding HD
From Jude Cotter
HD is a huge and still growing field. For currency of information (and because it’s easier!) we recommend the excellent HD FAQ at www.hdforindies.com
More information from Graeme Nattress
HD currently has two frame sizes - 1920x1080 and 1280x720. However, it's much more complex than that because of two things - some tape formats sub-sample and don't record the full rated resolution, and the nature of interlace.
HDCAM is nominally 1920x1080, and that's the size of image you get off the HDSDI ports, but it's stored on tape as 1440x1080, making it a subsampled format. HDCAM SR, the more expensive version of HDCAM does record the full 1920x1080
DVCProHD is 1280x1080 or 960x720 depending on version used. It subsamples further than HDCAM, but uses a lower bit rate too.
D5 is Panasonic's full raster 1920x1080 or 1280x720 format, but doesn't appear in any camcorder, but only as a deck for mastering to.
HDV comes in 1280x720 (ie full raster 720p) or 1440x1080 subsampled 1080i, like HDCAM.
Next there's the issue of interlace. 720p is always progressive, hence the p, and can range from 24 to 60 full frames per second depending on format. This makes every frame clean, and it compresses very well.
Most 1080 formats are 1080i. That means they're interlaced, so store each frame of 1920x1080 (or 1440x1080) as two fields of 1920x540. However, it's not as simple as that, as before each field is made it is vertically filtered which reduces it's resolution to about 70% of what it started with in an attempt to reduce the nasties of interlace flicker (twitter). This means that the measurable resolution of 1080i is something like 1920x700 or 1440x700 or so, so effectively a lot of pixels are wasted on blurred data, and given the issues of compressing interlaced video makes the overall video harder to compress.
Some 1080p formats are properly 1080p, and don't do interlace or it's vertical filtering and store the full resolution. These are mostly used for digital cinema, although it's still below what is normally considered the minium for cinema use - 2k.
There is also the HD Survival Handbook by Philip Hodgetts. It is a 212 page PDF and covers everything you need to know about HD Production.
Read all about it here:
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
What's the best workflow for working with HDV?
From Graeme Nattress:
Although many people recommend getting out of HDV as soon as you can, what is usually best for HDV is to edit nativly. Yes - this works fine, as Apple have done a superb job on the codec to make it work right. Then, right at the end of editing, you change the timeline to uncompressed, re-render, and output to your high end HD deck. Quality is maintained as best as possible throughout the whole process, and you don't need a massive raid while editing, only at the end.
Dubbing to HDCAM or DVCProHD might simplify workflows for some people, but is detrimental to image quality (and resolution if you dub to DVCProHD) - dubbing to D5 or HDCAM SR might be fine for quality as they're very lightly compressed, but the others are not. HDV even stores colour with a better sampling than HDCAM!
Also look at:
Apple has very good "White Papers" (PDF) on HDV Workflow including a FAQ. Download it here : Native HDV Editing with Final Cut Pro 5
Also read Charlie White's tutorial titled "Native HDV on Final Cut Pro 5"
and Capturing HDV into ProRes via Firewire by Andrew Balis.
and Capture HDV to ProRes in FCP? Over FireWire?! Yes! by Chris Poisson.
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
HDV won't play on an external monitor
From Michael Horton
HDV wont play out to an external monitor via Firewire. You need a Kona or Blackmagic Card. The Digital Cinema Desktop Preview is your only bet at this point.
Blackmagic Design has released a $249.00 HDMI card called the Intensity that will allow you to use your big screen television and/or video projector as a monitor by connecting to the built in HDMI-out. Find it at Decklink.com
To turn on Digital Cinema Desktop preview, go to View > Video Playback, and select the type of playback you want. Then select View > External > All Frames. To toggle this on and off, use apple - F12.
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
Upconverting DV to DVCPRO HD with Compressor
From Shane Ross:
Who made a nice simple video tutorial which you can see here : Uprezzing DV to DVCPRO HD
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
How does HDV work?
From Alister Robbie
HDV as a format is known as a long GOP format. GOP standing for Group Of Pictures. To understand the significance of this, we need to understand a GOP and a bit more about compression.
Let's start with intra-frame compression. This is compression inside a single frame - like a JPEG. It uses a bunch of algorithms to determine patterns and areas of similarity within the image so that it can ditch information without losing detail. From there we move to inter-frame compression where the compression algorithm starts comparing different frames within the clip to find similarities, and therefor ditch a bunch of data without losing detail.
When you use inter-frame compression, it uses three kinds of frames referred to as "I" "B" and "P" frames. Think of the 'I' frames as complete frames - nothing missing. 'P' frames contain only the data that has changed since the last frame, 'B' frames looks at the frame before and the frame afterwards to see what has changed in either direction, and only saves that. 'B' frames are useful for when you are shuttling backwards through the footage.
Now that we know what I, B & P frames are, we can look understand a GOP. A GOP is a group of I, B & P frames that form a small piece of video. For example, your HDV codec uses a "long GOP" structure which looks like "IBBPBBPBBPBBP" and it then repeats this structure again. The significance of this is that there is only one complete frame of information every 12 frames. This means that it takes up very little space, but will cause some issues which I will get into later.
Now we compare that to most other formats/codecs designed for editing such as DV, DVCPRO, Digital Betacam etc. These formats use what are referred to as "I frame only" compression which means that every frame is a complete frame. This takes up a lot more space, but is better for cutting.
If you want to make a cut in HDV, technically, you can only make a cut on an I (complete) frame. If you cut on a non-I frame, you will break the GOP structure, and there will be a group of frames that do not have an I frame to refer to. You will momentarily lose the signal when the clip is played back. Compare this to DV, where you can happily cut wherever you want, and you can start to see how issues might arise.
Given that people want to edit with HDV, Apple came up with few tricks to get around this issue. When you are cutting with HDV, Final Cut will allow you to make cuts on non-I frames. What the system does is in the background is at that cut point, it steps back to the last I frame and grabs that data, and adds it to the cut point so that all of the frames after that shot have an I frame to reference off. This happens everytime you make a cut in HDV.
This means that your original IBBPBBPBBPBBP GOP structure might now look something like IBBPBIBBPIBIBIPIIBBPI. This is now outside the boundaries of what your HDV deck will handle, and so once you are finished, and output, Final Cut Pro goes through a process where it re-orders all of the frames, and smooths things out. It makes sure that everything is in order and that it looks like the proper IBBPBBPBBPBBP.
If you change your sequence settings to another codec such as DVCPRO HD or 10bit Uncompressed (my favourite) it will force all of your long GOP HDV footage to become I frame only making it less processor intensive for your machine to work with.
For more information check out : The HDV Wiki
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
How do I work with P2 media?
Here's a great simple video tutorial about P2 import by Shane Ross : Importing P2 into FCP
Updated for FCP6:
- Importing P2 into FCP6 by Shane Ross
Also:
- Problems Mounting P2 Volumes by Andrew Balis
Also:
From Shane Ross:
THIS SITE is where you can download all the drivers for P2 and the applications that Panasonic provides for P2. It is compiled by Jon Kline.
From Strypes
For those of you who like reading, Panasonic has a pdf available.
How to work with P2 in FCP:
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
4:3 (NTSC) Title/Action safe Template in a 16:9 frame for both 720 & 1080 formats
From Joey "grafixjoe" Morelli
These are HD Square pixel frames with 4:3 (NTSC) title / action safe guides on them. The first one is 1280 x 720 and the second is 1920 x 1080. Drag them right out of this window onto your desktop, import it into your FCP Project, lay it in your timeline over all clips & add the "Screen" Composite Mode to get rid of the black leaving the guides only.
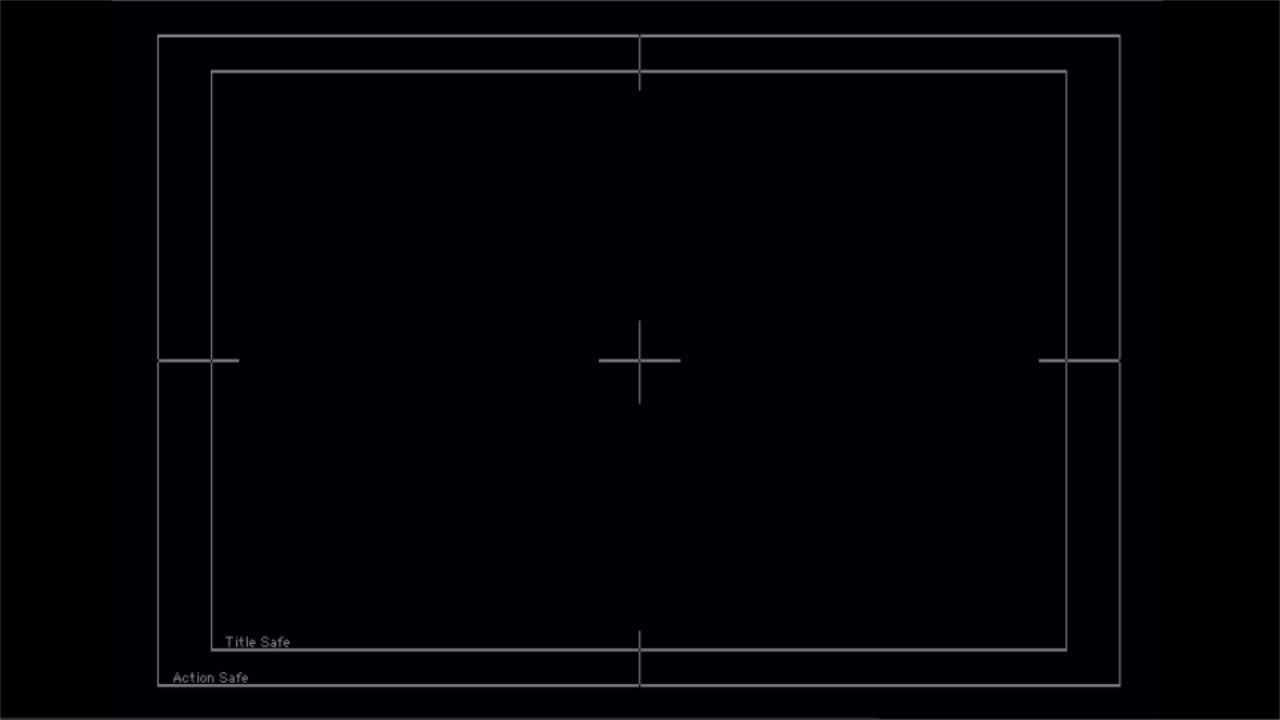
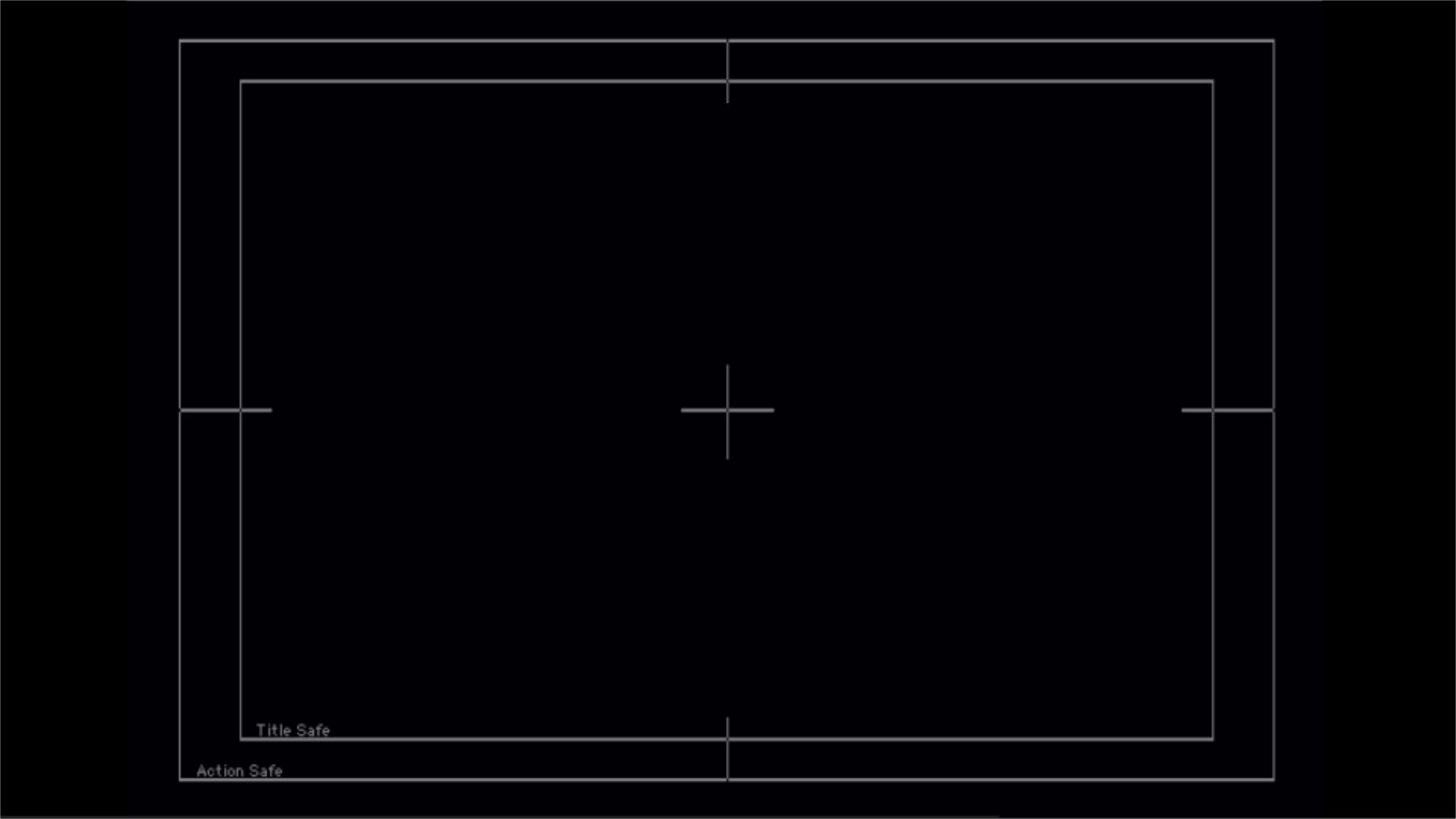
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
After upgrading to FCP 6.0.2 Log & Transfer no longer works
From Michael Horton
If you have Noise Industries FX Factory plugins, either v1.0.7 or v2.0, then this prevents LOG AND TRANSFER from working.
The solution is to download FX Factory version 2.0.1 from Noise Industries. It is a free upgrade to version 2.0 owners.
Download it here : noiseindustries.com
Apple Knowledge Base article: Final Cut Pro 6: Log and Transfer may fail if "FxFactory" is installed
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
I'm having problems with mounting XDCAM Volumes
From Michael Horton
Read this article from Andrew Balis.
also:
also:
and
From Jude Cotter
Here's a nice short video that steps through the standard process for importing EX1 clips into FCP : XDCAM EX and Final Cut Pro (FCP)
Also, Get Software updates here:
Also purchase:
and
From Michael Horton
Read this article by Rick Young:
and this by Matt Jeppsen
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
What files are required to work with P2?
From Strypes
Final Cut Pro's Log and Transfer requires the entire directory to be present to work properly with P2 media, including the LASTCLIP.TXT file. By default, the "PROXY" and "VOICE" folders are empty. The "AUDIO" folder contains the audio recorded in the camera, the "VIDEO" folder contains the video clips, the "ICON" folder contains thumbnails, and the "CLIP" folder contains XML files with the required metadata to sync up the video and audio files.
Here is a breakdown of the directory structure:
<Card Name>
LASTCLIP.TXT
<CONTENTS>
<AUDIO>
<CLIP>
<ICON>
<PROXY>
<VIDEO>
<VOICE>
Back to HD Formats FAQs Contents
Back to Index of FAQs
Back to lafcpug.org
